Next video is a react component for adding video to your next.js application. It extends both the <video> element and your Next app with features for automatic video optimization.
- Smart storage: Store large video files outside of your git repo
- Auto optimized: Automatically optimize video files and deliver via CDN for better playback performance and quality
- Customizable UI: Choose from themes or build your own player controls
- Posters & Previews: Zero-config placeholder images and timeline hover thumbnails
- Wider compatibility: Use videos that aren’t supported natively by all browsers
- Analytics built-in (optional): See how often videos get watched and track video performance
- AI-powered: Whisper captions coming soon...
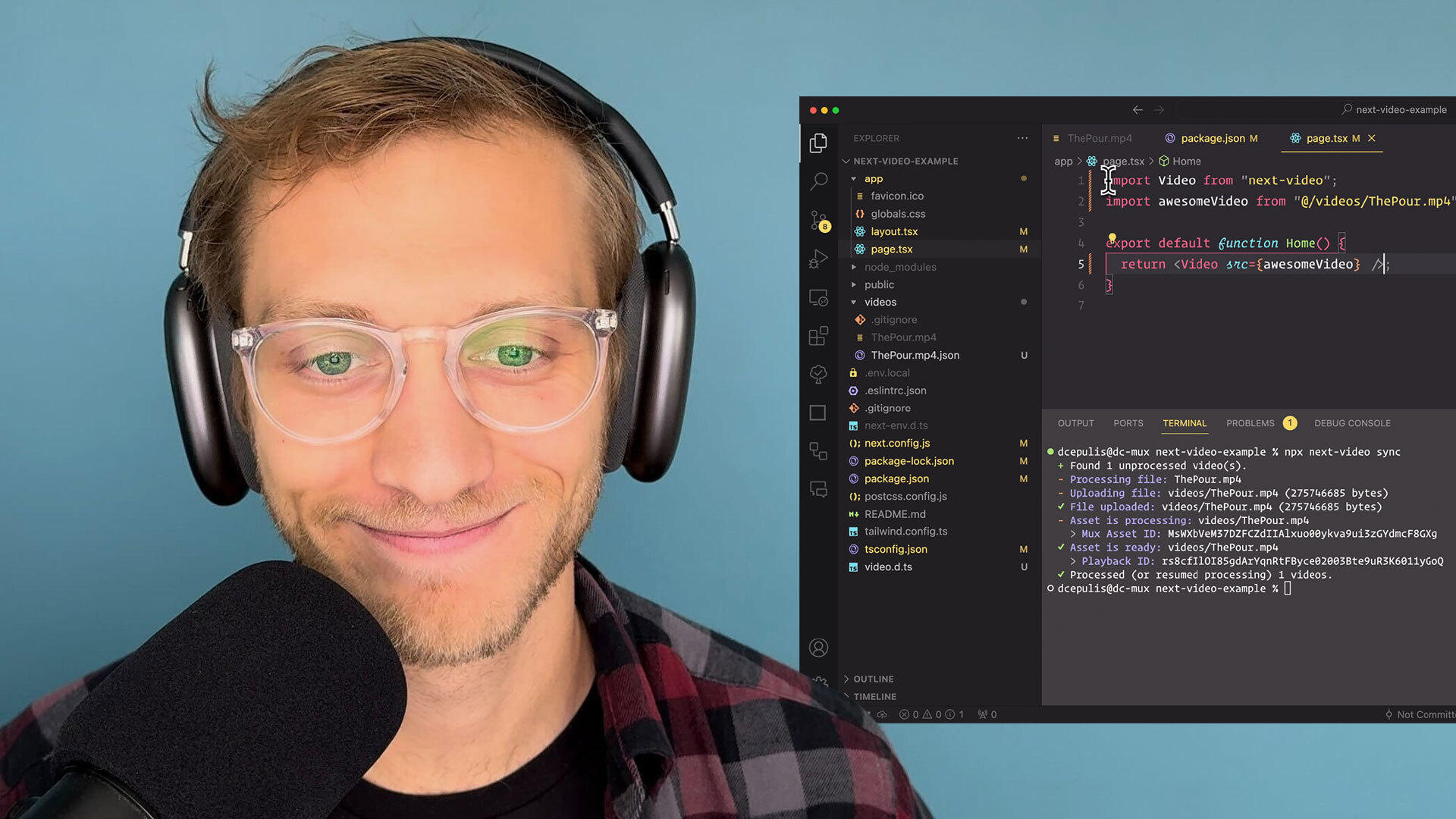
import Video from 'next-video';
import myVideo from '/videos/my-video.mp4';
export default function Page() {
return <Video src={myVideo} />;
}Setup
Install the package
cd your-next-app
# If your project is using NPM (the default for Next.js)
npm install next-video
# If your project is using Yarn
yarn add next-video
# If your project is using pnpm
pnpm add next-videoRun the init wizard
npx next-video initThis will (with prompting):
- install
next-videoas a dependency - update your
next.config.jsfile - if you're using TypeScript, add types for your video file imports
- create a
/videosdirectory in your project which is where you will put all video source files.
It will also add a .gitignore file to the /videos directory that ignores video files. Videos, particularly any of reasonable size, shouldn't be stored/tracked by git. Alternatively, if you'd like to store the original files you can remove the added gitignore lines and install git-lfs.
Remote storage and optimization
Vercel recommends using a dedicated content platform for video because video files are large and can lead to excessive bandwidth usage. By default, next-video uses Mux, which is built by the the creators of Video.js, powers popular streaming apps like Patreon, and whose video performance monitoring is used on the largest live events in the world.
- Sign up for Mux
- Create an access token
- Add environment variables to
.env.local(or however you export local env variables)
# .env.local
MUX_TOKEN_ID=[YOUR_TOKEN_ID]
MUX_TOKEN_SECRET=[YOUR_TOKEN_SECRET]OPTIONAL Manual Setup
If you choose to do any of the init steps manually.
Add Next Video to next.config.js
/** @type {import('next').NextConfig} */
const { withNextVideo } = require('next-video/process');
const nextConfig = {}; // Your current Next Config object
module.exports = withNextVideo(nextConfig);Add video import types to tsconfig.json
This is only required if you're using TypeScript, and makes sure your video file imports don't yell at you for missing types. video.d.ts should have been created in your project root when you ran npx next-video init, if not you can create it manually:
// video.d.ts
/// <reference types="next-video/video-types/global" />Then add that file to the include array in tsconfig.json.
{
// ...
"include": ["video.d.ts", "next-env.d.ts", /* ... */ ]
// ...
}Usage
Local videos
Add videos locally to the /videos directory then run npx next-video sync. The videos will be automatically uploaded to remote storage and optimized. You'll notice /videos/[file-name].json files are also created. These are used to map your local video files to the new, remote-hosted video assets. These json files must be checked into git.
npx next-video syncYou can also add next-video sync -w to the dev script to automatically sync videos as they're added to /videos while the dev server is running.
// package.json
"scripts": {
"dev": "next dev & npx next-video sync -w",
},Now you can use the <Video> component in your application. Let's say you've added a file called awesome-video.mp4 to /videos
import Video from 'next-video';
import awesomeVideo from '/videos/awesome-video.mp4';
export default function Page() {
return <Video src={awesomeVideo} />;
}While a video is being uploaded and processed, <Video> will attempt to play the local file. This only happens during local development because the local file is never uploaded to your git repo.
Remote videos
For videos that are already hosted remotely (for example on AWS S3), import the remote URL and refresh the page.
This creates a local JSON file in the /videos folder and the sync script will start uploading the video.
import Video from 'next-video';
import awesomeVideo from 'https://www.mydomain.com/remote-video.mp4';
export default function Page() {
return <Video src={awesomeVideo} />;
}If the hosted video is a single file like an MP4, the file will be automatically optimized for better deliverability and compatibility.
Alternative
In some cases you might not have the remote video URL's available at the time of import.
That can be solved by creating a new API endpoint in your Next.js app for /api/video with the following code.
App router (Next.js >=13)
// app/api/video/route.js
export { GET } from 'next-video/request-handler';Pages router (Next.js)
// pages/api/video/[[...handler]].js
export { default } from 'next-video/request-handler';Then set the src attribute to the URL of the remote video, refresh the page and the video will start processing.
import Video from 'next-video';
export default function Page() {
return <Video src="https://www.mydomain.com/remote-video.mp4" />;
}Custom Player
You can customize the player by passing a custom player component to the as prop.
The custom player component accepts the following props:
asset: The asset that is processed, contains useful asset metadata and upload status.src: A string video source URL if the asset is ready.poster: A string image source URL if the asset is ready.blurDataURL: A string base64 image source URL that can be used as a placeholder.
import Video from 'next-video';
import { ReactPlayerAsVideo } from './player';
import awesomeVideo from '/videos/awesome-video.mp4';
export default function Page() {
return <Video as={ReactPlayerAsVideo} src={awesomeVideo} />;
}// player.js
import ReactPlayer from 'react-player';
export function ReactPlayerAsVideo(props) {
let { asset, src, poster, blurDataURL, ...rest } = props;
let config = { file: { attributes: { poster } } };
return <ReactPlayer url={src} config={config} {...rest} />;
}Hosting & Processing Providers
You can choose between different providers for video processing and hosting.
The default provider is Mux.
To change the provider you can add a provider option in the next-video config.
Some providers require additional configuration which can be passed in the providerConfig property.
// next.config.js
const { withNextVideo } = require('next-video/process');
/** @type {import('next').NextConfig} */
const nextConfig = {};
module.exports = withNextVideo(nextConfig, {
provider: 'backblaze',
providerConfig: {
backblaze: { endpoint: 'https://s3.us-west-000.backblazeb2.com' }
}
});Supported providers with their required environment variables:
| Provider | Environment vars | Provider config | Pricing link |
|---|---|---|---|
mux (default) | MUX_TOKEN_IDMUX_TOKEN_SECRET | Pricing | |
vercel-blob | BLOB_READ_WRITE_TOKEN | Pricing | |
backblaze | BACKBLAZE_ACCESS_KEY_IDBACKBLAZE_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY | endpointbucket (optional) | Pricing |
amazon-s3 | AWS_ACCESS_KEY_IDAWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY | endpointbucket (optional) | Pricing |
| More coming... |
Provider feature set
| Mux (default) | Vercel Blob | Backblaze | Amazon S3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Off-repo storage | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Delivery via CDN | ✅ | ✅ | - | - |
| BYO player | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Compressed for streaming | ✅ | - | - | - |
| Adapt to slow networks (HLS) | ✅ | - | - | - |
| Automatic placeholder poster | ✅ | - | - | - |
| Timeline hover thumbnails | ✅ | - | - | - |
| Stream any soure format | ✅ | - | - | - |
| AI captions & subtitles | ✅ | - | - | - |
| Video analytics | ✅ | - | - | - |
| Pricing | Minutes-based | GB-based | GB-based | GB-based |
Required Permissions for Amazon S3
If you're using Amazon S3 as the provider, you'll need to create a new IAM user with the following permissions:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:ListAllMyBuckets",
"s3:CreateBucket",
"s3:PutBucketOwnershipControls"
],
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:PutBucketPublicAccessBlock",
"s3:PutBucketAcl",
"s3:PutBucketCORS",
"s3:GetObject",
"s3:PutObject",
"s3:PutObjectAcl",
"s3:ListBucket"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::next-videos-*"
}
]
}Roadmap
v0
- Automatic video optimization
- Delivery via a CDN
- Automatically upload and process local source files
- Automatically process remote hosted source files
v1
- Customizable player
- Connectors for additional video services
- AI captions
Trying it out locally
If you want to develop on this thing locally, you can clone and link this sucker. Just know...it's not a great time right now.
- Clone this repo
cdinto the reponpm install && npm run buildcd ../(or back to wherever you want to create a test app)npx create-next-appcd your-next-appnpx link ../next-video(or wherever you cloned this repo)